This article is written based on a previous work of firmware reverse engineering done by security researchers.
I bought a smart bulb (TP-LINK KL110) from amazon to connect it with my alexa echo dot, at the beginning that was the objective. Then I ask myself how this smart bulb works and how we can control it ?
TP-Link Smart Plug Protocol is a protocol employed by TP-Link used by the most of their smart devices available on the port 9999 for both TCP and UDP it’s a JSON-based protocol used for :
- Device discovery
- Device configuration
- Polling and/or modifying device state
Example of devices used this protocol

- HS110: Kasa Smart Wi-Fi Plug with Energy Monitoring
- NC250: TP-Link Wireless Security Camera

- KL110: TP-Link Kasa Smart Wi-Fi Light Bulb
Example of commands
Below is an example of commands to control the smart bulb.
Gets the system information for the light bulb.
Command:
{"system":{"get_sysinfo":{}}}
Returns:
{
"system":{
"get_sysinfo":{
"sw_ver":"1.8.11 Build 191113 Rel.105336",
"hw_ver":"1.0",
"model":"KL110(EU)",
"description":"Smart Wi-Fi LED Bulb with Dimmable Light",
"alias":"KITCHEN_LAMP",
"mic_type":"IOT.SMARTBULB",
"dev_state":"normal",
"mic_mac":"B095753C3D36",
"deviceId":"8012531BB5C0C0928D46BBC5C7AB84041CC581C9",
"oemId":"775B67C11038B99BEEDE39B0C910F6E9",
"hwId":"111E35908497A05512E259BB76801E10",
"is_factory":false,
"disco_ver":"1.0",
"ctrl_protocols":{
"name":"Linkie",
"version":"1.0"
},
"light_state":{
"on_off":1,
"mode":"normal",
"hue":0,
"saturation":0,
"color_temp":2700,
"brightness":75
},
"is_dimmable":1,
"is_color":0,
"is_variable_color_temp":0,
"preferred_state":[
{
"index":0,
"hue":0,
"saturation":0,
"color_temp":2700,
"brightness":100
},
{
"index":1,
"hue":0,
"saturation":0,
"color_temp":2700,
"brightness":75
},
{
"index":2,
"hue":0,
"saturation":0,
"color_temp":2700,
"brightness":25
},
{
"index":3,
"hue":0,
"saturation":0,
"color_temp":2700,
"brightness":1
}
],
"rssi":33,
"active_mode":"none",
"heapsize":336184,
"err_code":0
}
}
}
Turn on the bulb.
Command:
{"smartlife.iot.smartbulb.lightingservice":{"transition_light_state":{"on_off":1,"transition_period":0}}}
Returns:
{
"smartlife.iot.smartbulb.lightingservice":{
"transition_light_state":{
"on_off":1,
"mode":"normal",
"hue":0,
"saturation":0,
"color_temp":2700,
"brightness":75,
"err_code":0
}
}
}
How The Protocol works ?
The protocol TP-Link Smart Plug employs an algorithm to obfuscate the command, XOR each byte of the command to execute. Initial byte is XORed with special value 171.
def encrypt(string):
key = 171
result = pack('>I', len(string))
for i in string:
a = key ^ ord(i)
key = a
result += bytes([a])
return result
XOR is a weak cryptographic system, simply invert the algorithm above.
def decrypt(string):
key = 171
result = ""
for i in string:
a = key ^ i
key = i
result += chr(a)
return result
Gather all these informations together we can conclude that we can communicate with the smart bulb on the port 9999 by sending the json based command encrypted with the above algorithm.
So, first of all we connect to the bulb using its wifi open access point.

Then with a simple nmap scan using the port 9999 we can identify the bulb ip address.

Now, we have all the necessary information to control the smart bulb.
DEMO
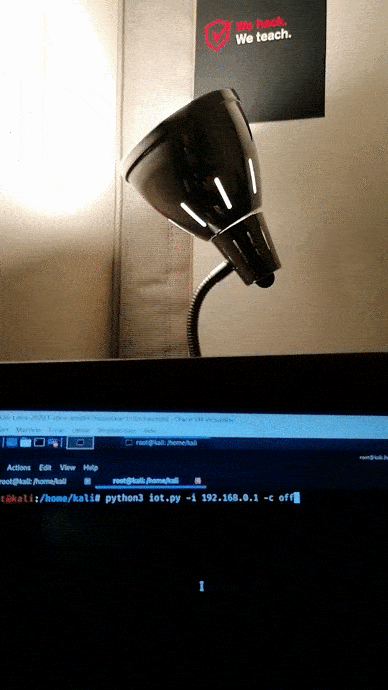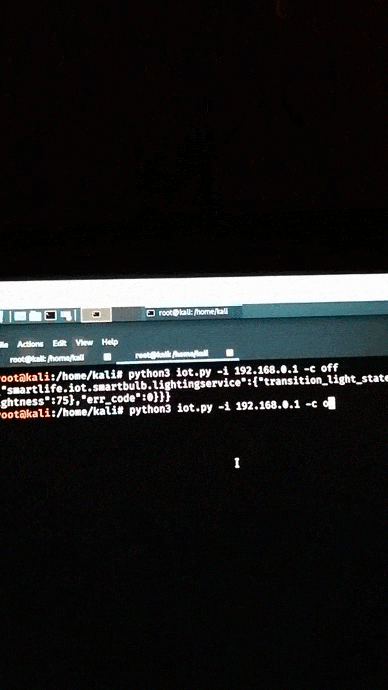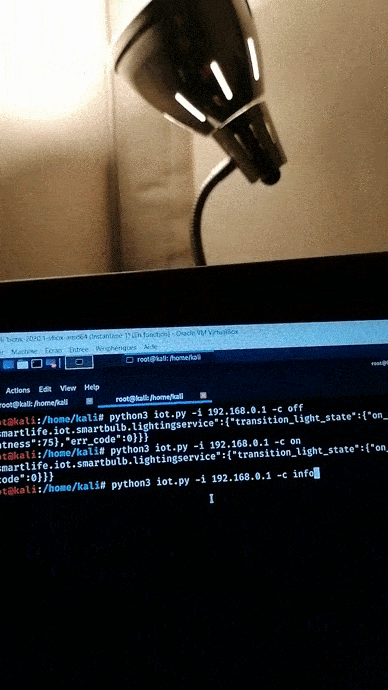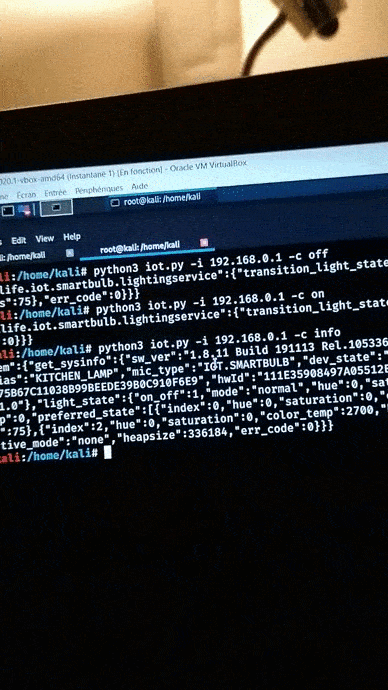
Check the video on YouTube
Source code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import socket
import argparse
from struct import pack
commands = { 'info' : '{"system":{"get_sysinfo":{}}}',
'on' : '{"smartlife.iot.smartbulb.lightingservice": { "transition_light_state": { "on_off": 1, "transition_period": 0 } }}',
'off' : '{"smartlife.iot.smartbulb.lightingservice": { "transition_light_state": { "on_off": 0, "transition_period": 0 } }}',
'set_alias': '{"smartlife.iot.common.system":{"set_dev_alias":{"alias":"KITCHEN_LAMP"}}}'
}
def encrypt(string):
key = 171
result = pack('>I', len(string))
for i in string:
a = key ^ ord(i)
key = a
result += bytes([a])
return result
def decrypt(string):
key = 171
result = ""
for i in string:
a = key ^ i
key = i
result += chr(a)
return result
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="TP-Link Wi-Fi Smart Plug Client")
parser.add_argument("-i", "--ip", metavar="<ip>", required=True, help="Target IP Address")
group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group(required=True)
group.add_argument("-c", "--command", metavar="<command>", help="Preset command to send. Choices are: "+", ".join(commands), choices=commands)
args = parser.parse_args()
ip = args.ip
port = 9999
if args.command is None:
cmd = args.json
else:
cmd = commands[args.command]
try:
sock_tcp = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock_tcp.connect((ip, port))
sock_tcp.send(encrypt(cmd))
data = sock_tcp.recv(2048)
sock_tcp.close()
decrypted = decrypt(data[4:])
print(decrypted)
except socket.error:
quit("Could not connect to host " + ip + ":" + str(port))
Sources
https://www.troopers.de/downloads/troopers17/TR17fgont-iot_tp_link_hacking.pdf https://www.briandorey.com/post/tp-link-lb130-smart-wi-fi-led-bulb-python-control
