DVID (Damn Vulnerable IoT Device) is an open source IoT hacking learning board, a project created by Vulcainreo to make IoT hacking accessible for everyone. For more information visit the DVID website.
I have the opportunity to win a DVID board in a pentest competition by orange cyberdefense during the fic forum, lille 2020.

The bluetooth challenge
Here we will focus on one of the bluetooth training challenges.
Goal
- A confidential message is stored on the firmware but protected by a password
- The goal is to provide a screenshot of the confidential message
Tips
Come on to say hello on 0000ffe1
Result
The password is an animal name.
WTF is BLE
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a part of the Bluetooth 4.0 specification which additionally also includes Classic Bluetooth and Bluetooth High Speed Protocols. Compared to classic Bluetooth, BLE is intended to use lesser power while maintaining similar communication range.
BLE is a cheap and very insecure version of bluetooth, in which you have no channel hopping (all hail easy sniffing and MITM!) and no builtin protocol security.
Main 3 BLE vulnerabilities
- Eavesdropping
- Man in the Middle Attacks (MITM)
- Denial of Service & Fuzzing Attack
Core concepts in BLE
There are two basic concepts in BLE :
Generic Access Profile - GAP
GAP is responsible for the visibility of a device to the external world and also plays a major role in determining how the device interacts with other devices.
Generic Attribute Protocol - GATT
GATT determines how two BLE devices exchange data with each other using concepts - service and characteristic.
The two main concepts that form GATT are :
- Characteristics
Characteristics are the most fundamental concept within a GATT transaction. Characteristics contain a single data point and akin to services, each characteristic has a unique ID or UUID that distinguishes itself from the other characteristic. For example, you could have a service called “Heart Rate Monitor” that includes characteristics such as “heart rate measurement.”
- Services
Services are simply defined as a cabinet which can hold many drawers in it, which in turn are called as characteristics. A service can have many characteristics. Each service is unique in itself with a universally unique identifier (UUID) that could either be 16 bit in size for official adapted services or 128 bit for custom services.

Write up
First of all we need to prepare our vulnerable environment, the board core is composed by a Atmega328p and a OLED screen. For each challenge, a firmware could be flashed on the Atmega328p.
root@psycor:~# git clone https://github.com/Vulcainreo/DVID.git
root@psycor:~# cd DVID/trainings/bluetooth/characteristics2/
- Flash the firmware to the board
root@psycor:~# avrdude -c usbasp -p m328p -U flash:w:characteristics2.ino.arduino_standard.hex

-
Scan for BLE devices, here i will use an android app. You can also use ettercap on your linux machine
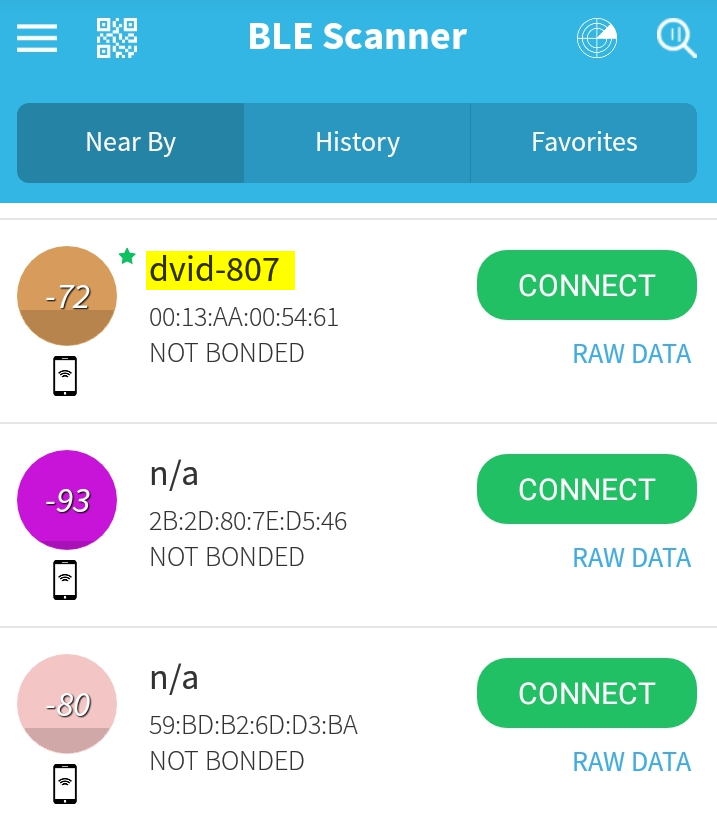
-
Connect to the DVID device and enumerate all the things
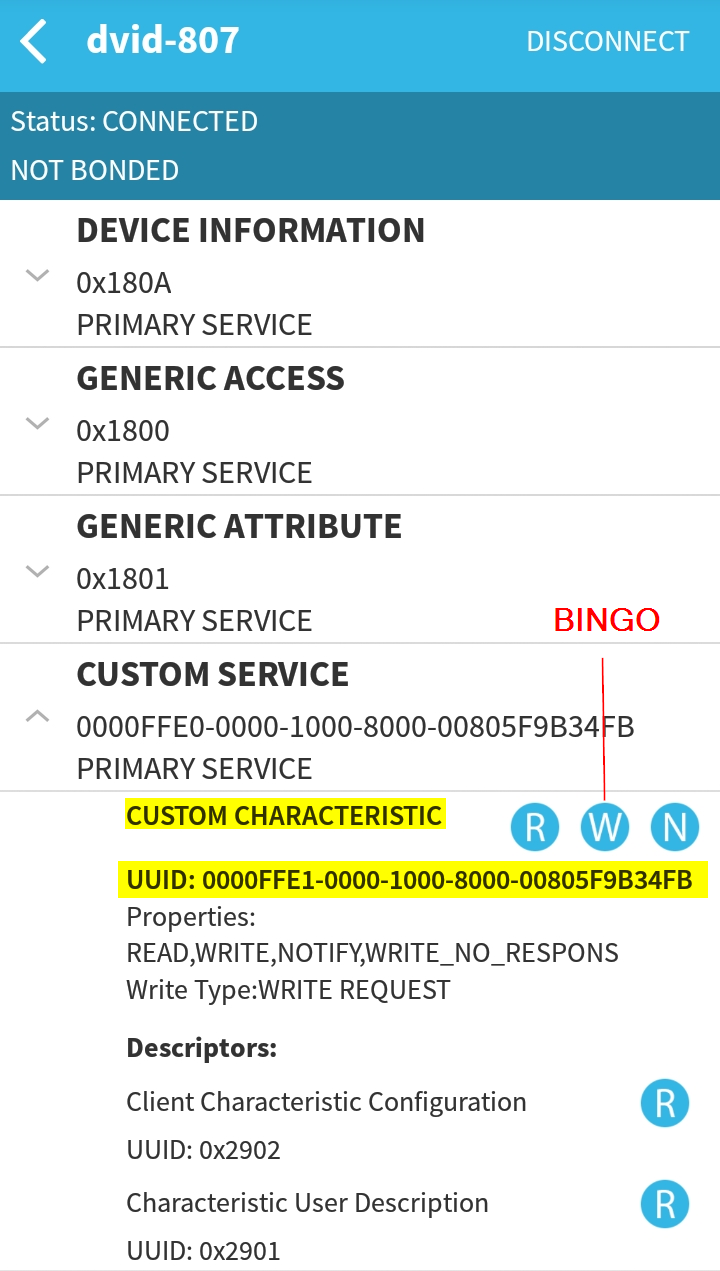
-
Write the bytes hello to the custom characteristic of the DVID device
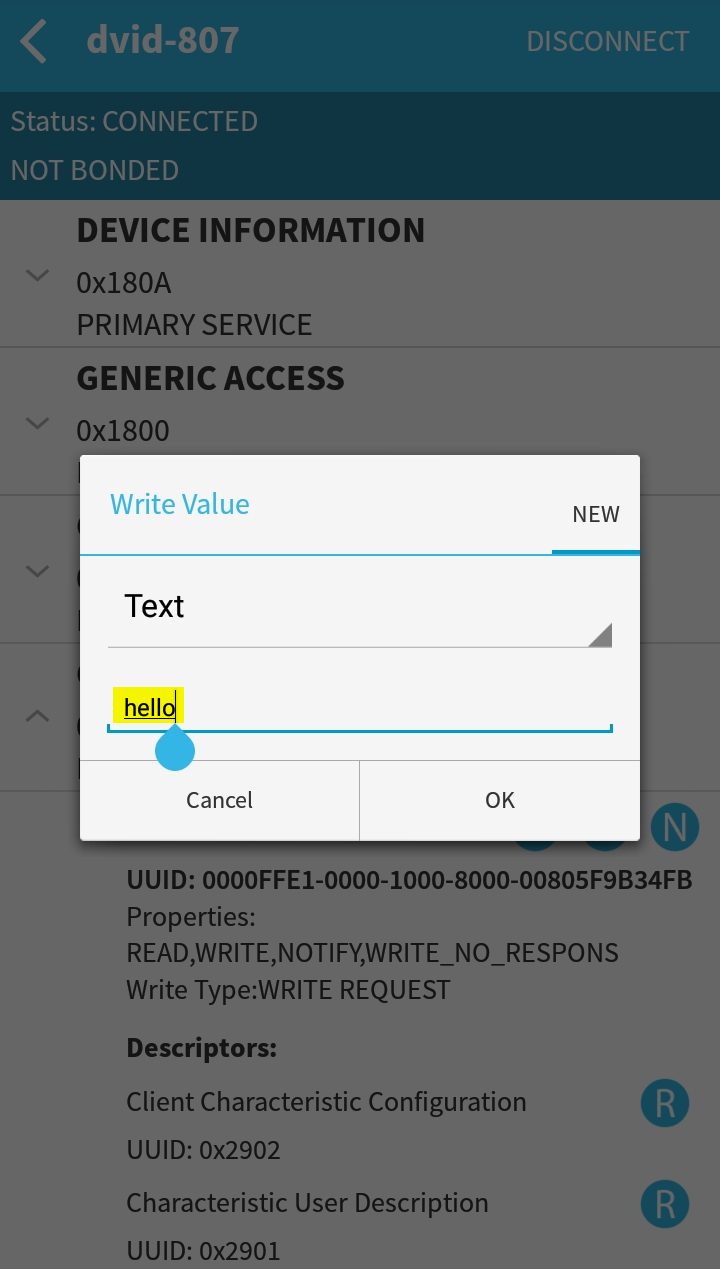
-
BINGO, We see the result on the screen :)

Sources
https://www.evilsocket.net/2017/09/23/This-is-not-a-post-about-BLE-introducing-BLEAH/ https://blog.attify.com/the-practical-guide-to-hacking-bluetooth-low-energy/
